This information is for healthcare professionals based in EU countries only.
Are you a healthcare professional?
"The diagnosis of hATTR should include DNA sequencing, biopsy, and amyloid typing. Following the diagnosis, patients should be followed up at regular intervals to monitor for disease progression1
In endemic areas, hATTR should be suspected in patients presenting with progressive sensory polyneuropathy or autonomic dysfunction, plus at least one red flag symptom suggestive of multisystemic involvement1
In non-endemic areas, hATTR should be considered for patients presenting with idiopathic, axonal polyneuropathy or atypical chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, plus at least one red flag symptom suggestive of multisystemic involvement1
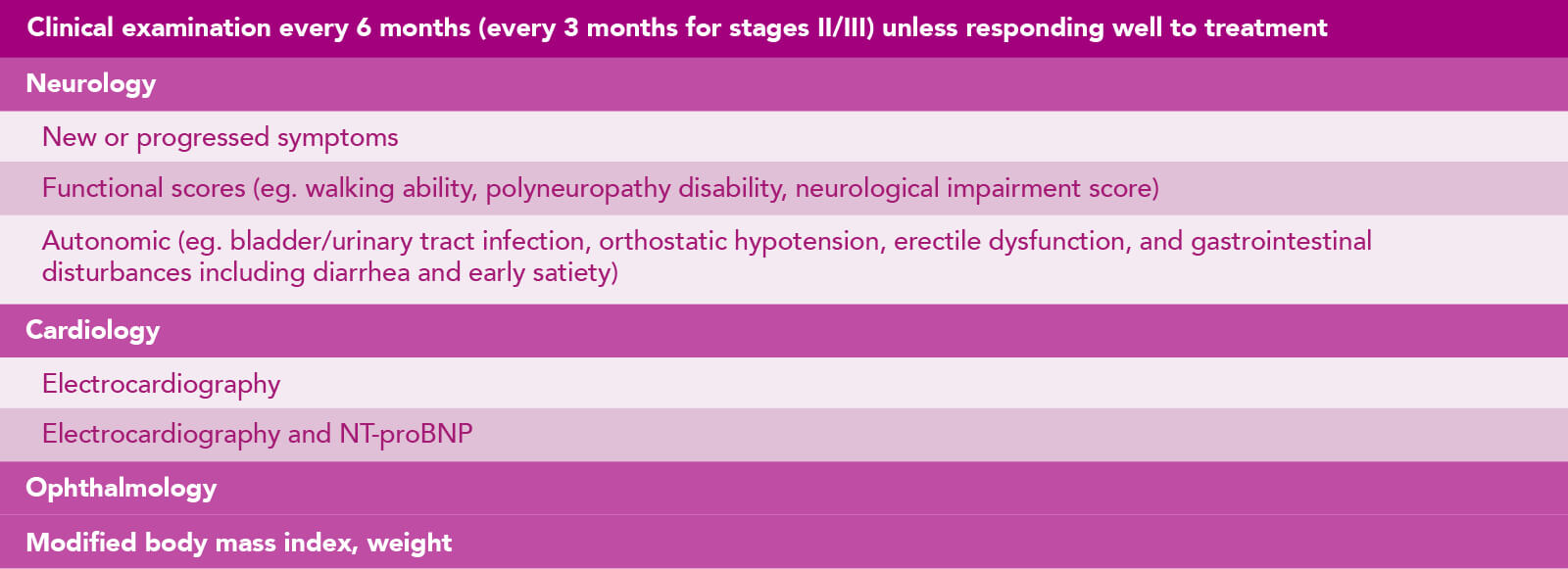
NT-proBNP N-terminal fragment of the pro b-type natriuretic peptide
This information is for healthcare professionals based in EU countries only.
Are you a healthcare professional?